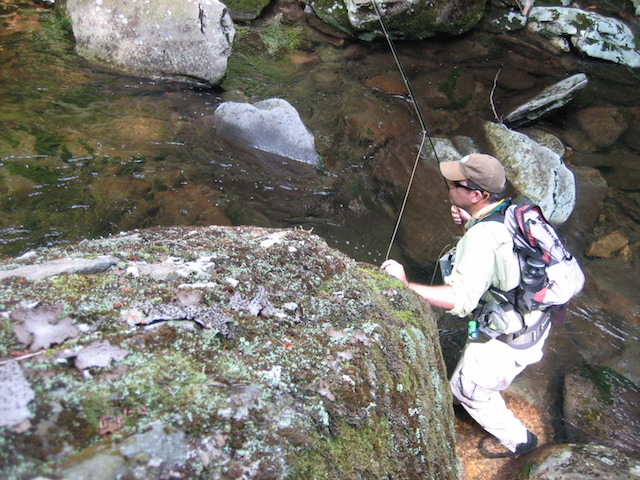
June is here and that means things begin to make another seasonal change here in the mountains. I always look forward to warmer weather because I get to shed the waders and enjoy the feel of cool mountain stream water on my legs and feet. I also enjoy the freedom of movement I have without waders. But the absence of waders also exposes you to a few more risks.
Mountain fishing involves moving. You move through the water, you move over boulders and you move through the woods where you encounter sharp sticks, prickly bushes and undergrowth, poison ivy, and a variety of critters. For these reasons, I always encourage people not to wear shorts when wet wading. A pair of long, synthetic “quick-dry” pants will provide you the same level of comfort while still giving your legs much needed protection.
Wading boots are also a must. I frequently see fishermen attempting to wet wade in Chacos or some other type of river sandals, and I cringe every time I do. A good pair of wading boots will not only provide you with the much-needed traction of felt soles (or Vibram), but will also offer ankle support and toe protection. You will definitely want both when navigating the rocky bottoms found in all mountain streams.
If you already have waders and boots, note that the boots are oversized to fit over the 3mm neoprene foot of the wader. Consider purchasing a pair of neoprene socks for wet wading. These will not only make your boots fit, they will provide a layer of padding and insulation.

Critters are another thing to be aware of when fishing in the summer months. Snakes are the biggest concern for most people but they aren’t much of an issue. While we do have two poisonous snakes in the Smokies, Copperheads and Timber Rattlesnakes, most of the snakes encountered by fishermen are harmless water snakes. I spend nearly 200 days a year in the park and probably see one or two poisonous snakes a year. The Great Northern Water Snake is a fairly large water snake that is often mistaken for a Cottonmouth, a species we do not have in the Smokies.

On a guide trip this spring, I came across a dead rattlesnake at the edge of the stream. Someone had obviously bashed its head in with a rock. There is absolutely no reason for this, and in the national park (and I believe the state of Tennesse), it is illegal. If you encounter a snake, poisonous or otherwise, just leave it alone and move on. They don’t want anything to do with you either.
What I try to keep an eye out for more than anything else, especially during the summer months, are hornet nests. They love to build these things on low branches above streams. If you see one, steer clear and move on to the next hole. And when you do, make sure it is still well out of range of your back cast. Hooking a hornet nest can ruin your day in a hurry.

If you do accidentally get too close and get stung, DO NOT start swatting! This triggers a pheromone that signals all other hornets in the area and one or two stings can turn into dozens. Just get far away from the nest as quickly as possible.
Yellow Jackets are also common in the Smokies and typically build their nests in the ground. As with snakes, your best solution here is just to pay attention and watch where you are stepping. Of course, if you are allergic to either of these, come prepared with an EpiPen or other treatment. If you’re not allergic, most stings can be easily treated by immediately and thoroughly rinsing the area. Applying an anti-itch medication will also provide relief.
Mosquitoes, noseeums, and other biting insects are not a huge problem when you’re on the stream but can be as soon as you step away from the stream in the woods or on the trail. On the stream, you’ll mostly just be harassed by gnats that don’t bite, but love to hover around your face and get in your eyes.
 The best prevention for all of these, of course, is good old-fashion bug spray. Bug sprays with higher concentrations of Deet seem to be most effective, but be careful when using them. Deet has the ability to melt plastic, and getting a healthy dose of Deet heavy bug spray on your fingers can wreck a fly line. Just avoid spraying it on your palms and finger tips. If you’re one who likes to spray your hands and rub it on your face, just spray the back of your hands and rub it in that way.
The best prevention for all of these, of course, is good old-fashion bug spray. Bug sprays with higher concentrations of Deet seem to be most effective, but be careful when using them. Deet has the ability to melt plastic, and getting a healthy dose of Deet heavy bug spray on your fingers can wreck a fly line. Just avoid spraying it on your palms and finger tips. If you’re one who likes to spray your hands and rub it on your face, just spray the back of your hands and rub it in that way.
Of course, anytime you’re maneuvering through  the woods, there’s a chance of picking up a tick. Deet based bug sprays will help with that, too. I still try to check myself periodically, particularly at the end of the day. If you do find one on you, there’s an easy way to remove it. Squeeze a dab of medicated lip balm (the gel type that comes in the squeeze tube) onto your finger and smear it on the tick. It will immediately release itself from your skin. Cool, huh?!? I always keep a tube of Carmex in my first aid kit for this reason.
the woods, there’s a chance of picking up a tick. Deet based bug sprays will help with that, too. I still try to check myself periodically, particularly at the end of the day. If you do find one on you, there’s an easy way to remove it. Squeeze a dab of medicated lip balm (the gel type that comes in the squeeze tube) onto your finger and smear it on the tick. It will immediately release itself from your skin. Cool, huh?!? I always keep a tube of Carmex in my first aid kit for this reason.
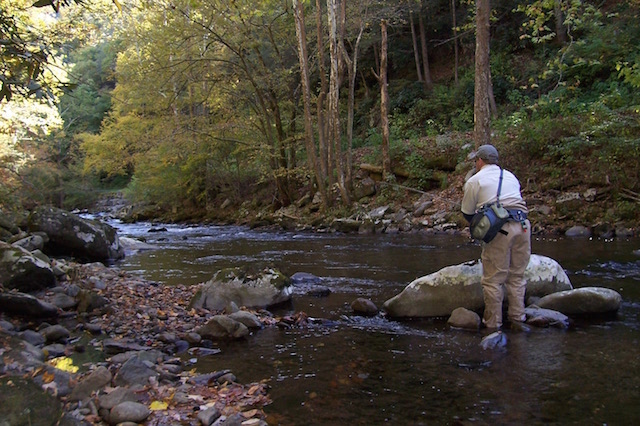
 Last month, I talked about ways to simplify your fly selection and offered tips on how to choose flies based on season and what was hatching. Based on the number of questions I had, however, I left out an important part of the process. Many folks said they are often uncertain when to fish a dry fly vs. a nymph.
Last month, I talked about ways to simplify your fly selection and offered tips on how to choose flies based on season and what was hatching. Based on the number of questions I had, however, I left out an important part of the process. Many folks said they are often uncertain when to fish a dry fly vs. a nymph.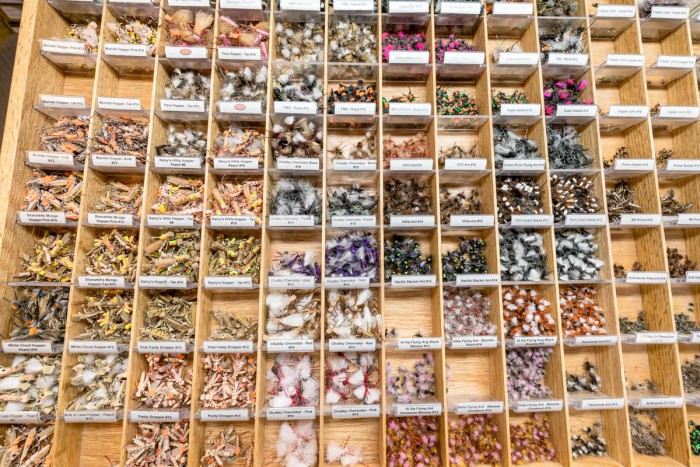 If you are new to fly fishing, particularly for trout, it is easy to be overwhelmed by the number of fly patterns available. Which ones do I need? What colors? What sizes? Do I need all of them? First of all, if you tried to carry every trout fly with you, you’d need a wheelbarrow to go fly fishing! While there is no way to make it immediately simple, there are ways to simplify the process. As with many things in fly fishing, you try to find a good starting point and learn as you go from there.
If you are new to fly fishing, particularly for trout, it is easy to be overwhelmed by the number of fly patterns available. Which ones do I need? What colors? What sizes? Do I need all of them? First of all, if you tried to carry every trout fly with you, you’d need a wheelbarrow to go fly fishing! While there is no way to make it immediately simple, there are ways to simplify the process. As with many things in fly fishing, you try to find a good starting point and learn as you go from there.
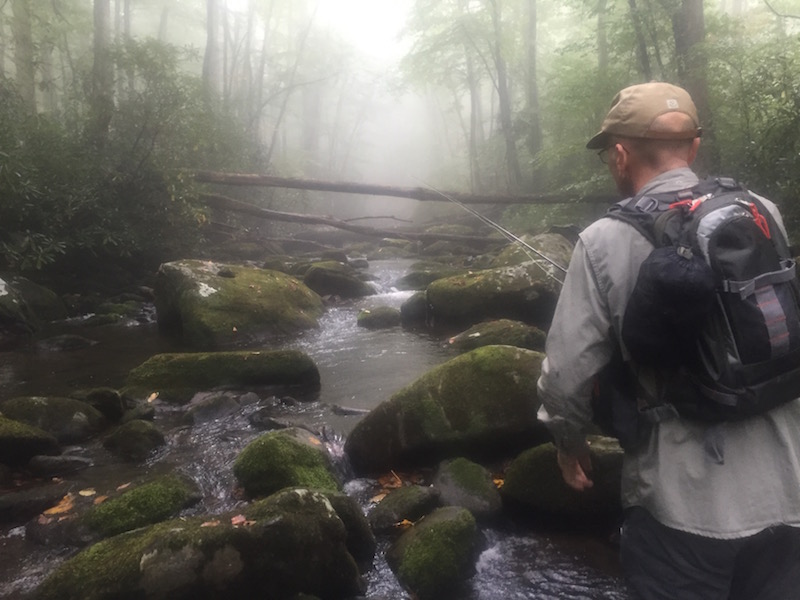


 As many of you know, I spend nearly 200 days a year fishing and guiding on small mountain streams in the Smoky Mountains where creel surveys indicate that approximately 90% of (unguided) fishermen never catch a fish. Meanwhile, the 10% who do catch fish tend to catch A LOT of them. When fishing small streams, it’s a fine line between getting skunked and catching 50, and most of the time, the difference isn’t what’s in your fly box. In the Smokies and other similar small mountain streams, approach and presentation is the name of the game and to have success, you may need to adjust a few of your techniques. Listed below are 10 tips that may make your next small stream fishing trip more productive.
As many of you know, I spend nearly 200 days a year fishing and guiding on small mountain streams in the Smoky Mountains where creel surveys indicate that approximately 90% of (unguided) fishermen never catch a fish. Meanwhile, the 10% who do catch fish tend to catch A LOT of them. When fishing small streams, it’s a fine line between getting skunked and catching 50, and most of the time, the difference isn’t what’s in your fly box. In the Smokies and other similar small mountain streams, approach and presentation is the name of the game and to have success, you may need to adjust a few of your techniques. Listed below are 10 tips that may make your next small stream fishing trip more productive.