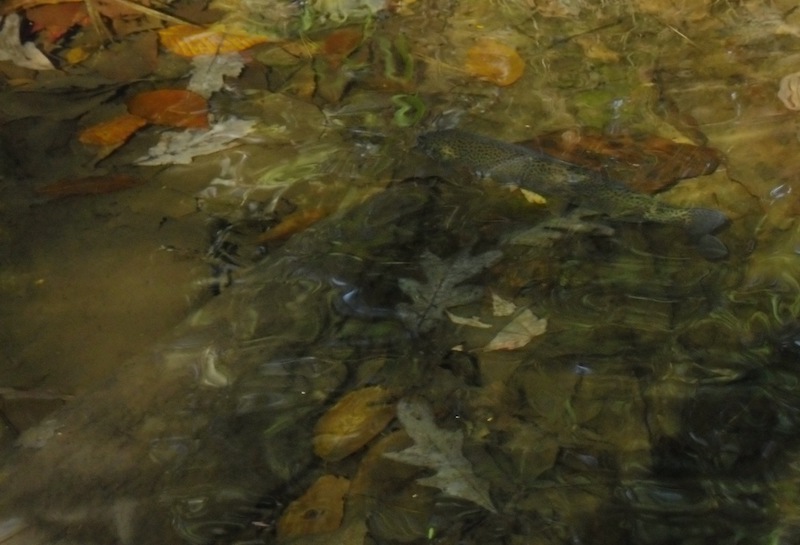
In some fly fishing scenarios, spotting fish is absolutely critical for success. Fishing the saltwater flats for bonefish, redfish, tarpon, etc. or the freshwater mud flats for carp will provide little more than casting practice if you can’t see the fish. In other scenarios, such as fishing a mountain trout stream, you can tell where fish should be by reading the water, and you can catch a lot of fish just by fishing likely spots. But even when fishing trout streams, the ability to spot fish in the water can sometimes allow you to locate and target larger fish. In the fall, this is particularly relevant in the Smokies as large brown trout begin moving into flatter, shallower water preparing to spawn.
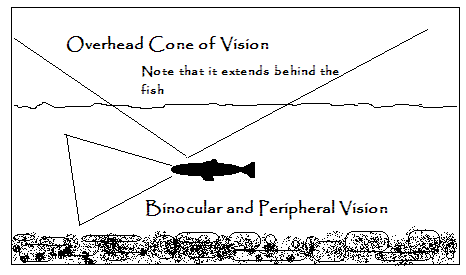
Spotting fish can be difficult to learn and there is no substitute for years of experience and practice, but there are a few things that can help you get started. The best place to start is with a pair of polarized sunglasses and this article will help a little when choosing a pair. The next thing to understand is how trout see, because as you seek out vantage points from which to spot fish, you want to avoid spooking the fish in the process. Here is an article on trout behavior that goes into a little more detail. Now we’re ready to go spot some fish.
Start by looking for fish in slower water. The more broken the surface is, the more difficult it will be to see through it. If possible, try to find a higher vantage point from which to look. This will greatly reduce the amount of light refraction from the water’s surface. Just remember that the higher up you get, the easier it will be for fish to pick up your movement. Avoid standing erect on a large boulder, as your silhouette will be far more pronounced. A high bank with a wooded backdrop is ideal, but you’ll still want to keep your movements slow and minimal. If you are on a large rock above a pool, get on your belly and peek over the edge. Remember the old westerns where the Indians were looking off the rocky bluffs about to attack the wagon train? That’s the idea.
Now that you’re in position, take your time. It’s extremely rare that you’re going to step up to a pool and immediately see a 27” brown trout. You have to methodically scan the pool. Start by reading the water and looking for fish where they should be. Look for obvious feeding areas in and around current lanes and foam lines. Look for areas with obvious cover under and around big rocks and/or fallen trees. They blend in REALLY well, so look long and hard and train your eye to look through the water rather than at it.
It’s hard. You’ll spot plenty of fish that turn out to be rocks or pieces of wood. I once spent 15 minutes casting to a plastic grocery bag hung on an underwater limb. It had the exact shape and movement of a trout! I was in the water and my buddy was above me, watching from a bridge. We were both certain it was a fish!

Movement and shape really are the best giveaways and that’s why it’s so important to take your time and give long looks to those likely spots. You may not see anything at first, then you see a little movement and suddenly the fish is visible. And once you spot one, you often begin to notice others around him. Watching the actual stream bottom, especially on sunnier days, can be helpful too. The movement that you often detect is the shadow of the fish.
Another thing to look for is a flash near the stream bottom. The eyes of a trout are positioned in such a way that they look slightly upward. When feeding on nymphs on the bottom, the trout has to angle his body to see below and will often “twist” his body when he eats the nymph. When this occurs, his white belly reflects light and produces a flash. This is always helpful when looking for fish, but especially in faster water.
All of this is easier the more familiar you are with the stream bottom. If you have a favorite pool, maybe one where you spooked a big fish before, keep going back there and looking. You will inevitably begin memorizing the stream bottom and will more quickly and easily be able to differentiate between rocks and fish. Again, it’s not easy and it takes time but like most things, the more you practice, the better you’ll get.
So, you’re starting to spot some fish… now what? Don’t just jump in and start casting the second you see a nice one. Keep watching. What is the fish doing? If you see a big fish just hugging the bottom, he’s not feeding and you’re wasting your time casting to him. But good news… you found a big fish. You might come back closer to dawn or dusk when he is more likely to be feeding.

If you spot a fish up in the water column, he’s likely feeding. Keep watching him. Is he looking up? Does he consistently feed to his right? Is he staying in one place or is he systematically rotating to different locations within the pool? Pay attention to all of these things and then you can plan your attack. Sometimes with big fish, you’re only going to get one shot and you want to make it count.
How much time you spend looking depends on you. I know guys that do little more than target big brown trout, and they spend far more time watching water than they do fishing. For me, it depends on where I’m fishing and the conditions. If I’m fishing pocket water on a high country brook trout stream, I’m not going to spend much time, if any, looking for big fish. I’m going to cover a lot of water and hit the likely spots. If I’m fishing a big pool on a brown trout river, I’m going to spend at least a few minutes looking before I jump in. If I’m fishing that same big pool in late fall, I’m going to look a lot more thoroughly!
 Probably 20 years ago, I was fishing the Clinch River with a buddy during the sulfur hatch. I won’t get into what has happened to that hatch, but back then, it was epic. Sulfurs would come off by the thousands for 4-6 hours a day for about 3 months. We would drive down from Kentucky to fish it and on most trips, we would both steadily catch fish, many topping 20”.
Probably 20 years ago, I was fishing the Clinch River with a buddy during the sulfur hatch. I won’t get into what has happened to that hatch, but back then, it was epic. Sulfurs would come off by the thousands for 4-6 hours a day for about 3 months. We would drive down from Kentucky to fish it and on most trips, we would both steadily catch fish, many topping 20”.
 If fish are actively rising but you don’t see any bugs in the air, check the water. Try to position yourself at the bottom of a feeding lane (downstream of where the fish are feeding) and watch the surface of the water (and just beneath) for drifting bugs. Holding a fine mesh net in the current is a great way to collect what’s coming down the channel, but if you don’t have one, your eyeballs will do just fine. If you see some insects, capture one and try to match it with a fly pattern.
If fish are actively rising but you don’t see any bugs in the air, check the water. Try to position yourself at the bottom of a feeding lane (downstream of where the fish are feeding) and watch the surface of the water (and just beneath) for drifting bugs. Holding a fine mesh net in the current is a great way to collect what’s coming down the channel, but if you don’t have one, your eyeballs will do just fine. If you see some insects, capture one and try to match it with a fly pattern.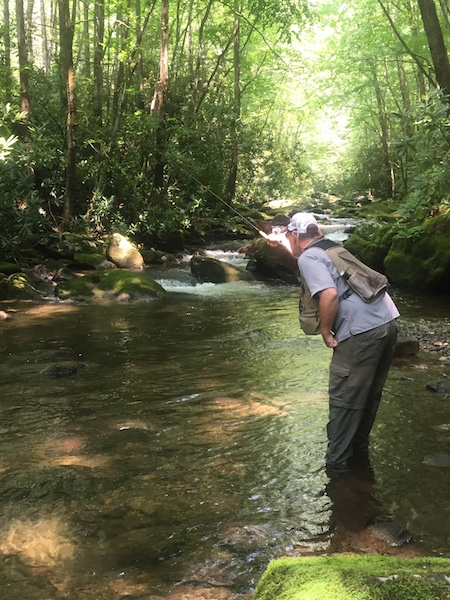
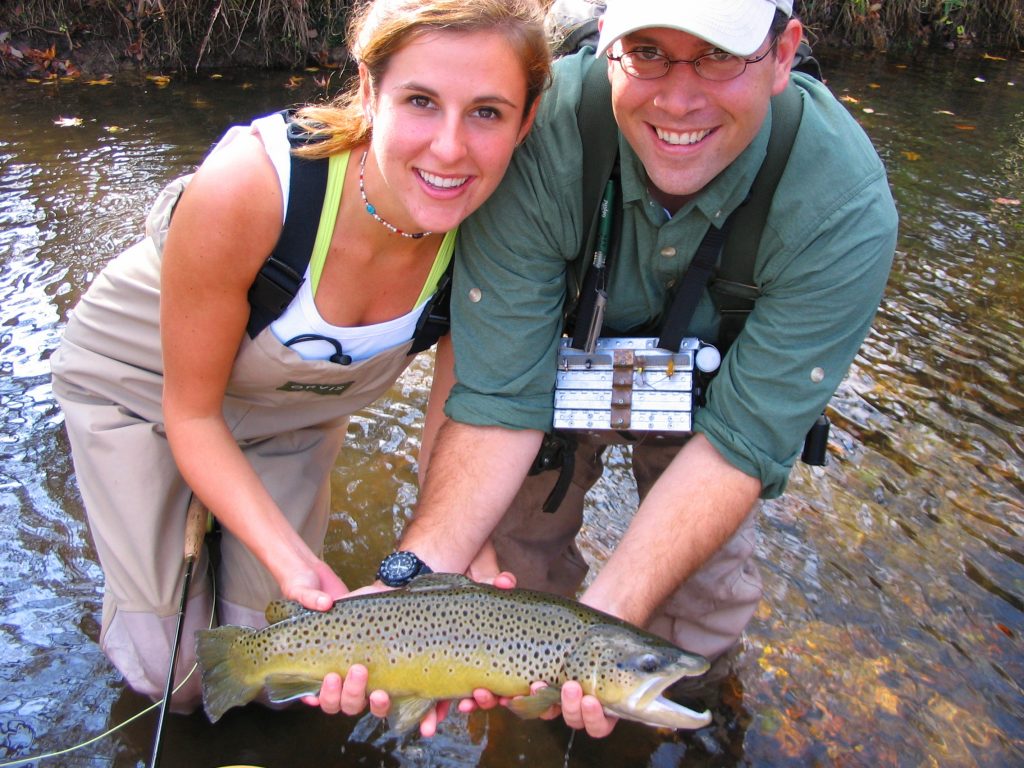

 It’s the time of year when certain folks seem to be whispering more at the fly shop. They’re isolated in corners and peeking over their shoulders before saying too much. They’re talking about brown trout. Big ones. Somebody mentioned seeing a decent one around Metcalf Bottoms – about 18-inches. A younger guy innocently asked, “Since when did we start referring to 18-inch browns as ‘decent’?” The older guy replied with a grin, “October.”
It’s the time of year when certain folks seem to be whispering more at the fly shop. They’re isolated in corners and peeking over their shoulders before saying too much. They’re talking about brown trout. Big ones. Somebody mentioned seeing a decent one around Metcalf Bottoms – about 18-inches. A younger guy innocently asked, “Since when did we start referring to 18-inch browns as ‘decent’?” The older guy replied with a grin, “October.” Fish that size don’t get caught often. Brown trout only live in a handful of rivers in the Smokies to begin with. They’re extremely cagey and for much of the year, they do most of their feeding at night – it’s illegal to fish the park at night. So, outside of the occasional big brown caught at dusk, or dawn, or after a good rain, we don’t get a lot of good shots at these guys. Until late fall.
Fish that size don’t get caught often. Brown trout only live in a handful of rivers in the Smokies to begin with. They’re extremely cagey and for much of the year, they do most of their feeding at night – it’s illegal to fish the park at night. So, outside of the occasional big brown caught at dusk, or dawn, or after a good rain, we don’t get a lot of good shots at these guys. Until late fall. Most people aren’t willing to put in the time it takes to catch one of these fish. Unless you’re just going to depend on luck, you have to trade fishing time for looking time. You may not spot one at the first place, or second or third… And once you do spot one, you’re not done looking. You have to watch him for a while to figure out his pattern: how he’s feeding, where he’s feeding, when he’s feeding, IF he’s feeding. You then may have to spend a pain-staking amount of time sneaking into a position where you can cast to him without spooking him.
Most people aren’t willing to put in the time it takes to catch one of these fish. Unless you’re just going to depend on luck, you have to trade fishing time for looking time. You may not spot one at the first place, or second or third… And once you do spot one, you’re not done looking. You have to watch him for a while to figure out his pattern: how he’s feeding, where he’s feeding, when he’s feeding, IF he’s feeding. You then may have to spend a pain-staking amount of time sneaking into a position where you can cast to him without spooking him. As many of you know, I spend nearly 200 days a year fishing and guiding on small mountain streams in the Smoky Mountains where creel surveys indicate that approximately 90% of (unguided) fishermen never catch a fish. Meanwhile, the 10% who do catch fish tend to catch A LOT of them. When fishing small streams, it’s a fine line between getting skunked and catching 50, and most of the time, the difference isn’t what’s in your fly box. In the Smokies and other similar small mountain streams, approach and presentation is the name of the game and to have success, you may need to adjust a few of your techniques. Listed below are 10 tips that may make your next small stream fishing trip more productive.
As many of you know, I spend nearly 200 days a year fishing and guiding on small mountain streams in the Smoky Mountains where creel surveys indicate that approximately 90% of (unguided) fishermen never catch a fish. Meanwhile, the 10% who do catch fish tend to catch A LOT of them. When fishing small streams, it’s a fine line between getting skunked and catching 50, and most of the time, the difference isn’t what’s in your fly box. In the Smokies and other similar small mountain streams, approach and presentation is the name of the game and to have success, you may need to adjust a few of your techniques. Listed below are 10 tips that may make your next small stream fishing trip more productive.
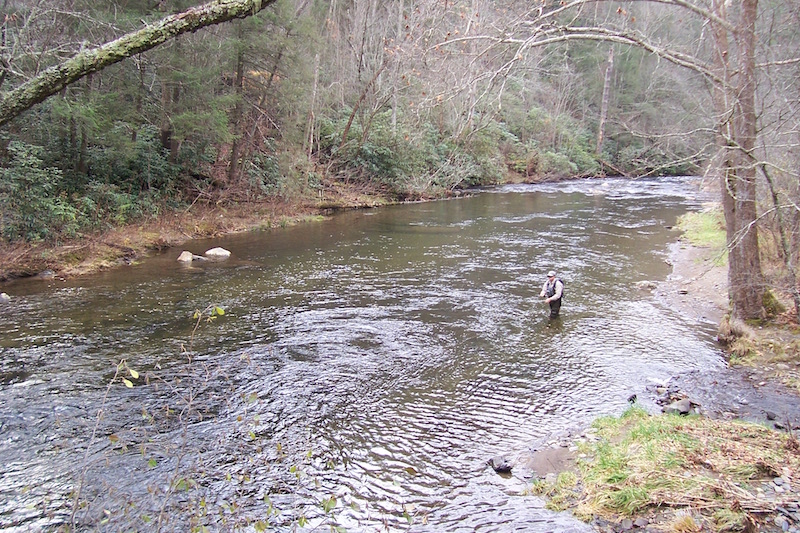





 Check out the photo above – a typical stretch of water in the Smokies. You can easily see the numerous changes in current speed and direction in just this small area. Rather than standing at the bottom right of the photo and casting 40-50 feet to the top left of the photo, our angler is intelligently breaking this stretch into defined sections. He has likely already fished the water below, to his left, and right in front of him. Notice he has his rod high, keeping the line off the current directly in front of him, and allowing the fly to drift nicely in the current breaking around the right of the boulder. Next, he will likely step up to the boulder and fish that large pocket above it. Well done!
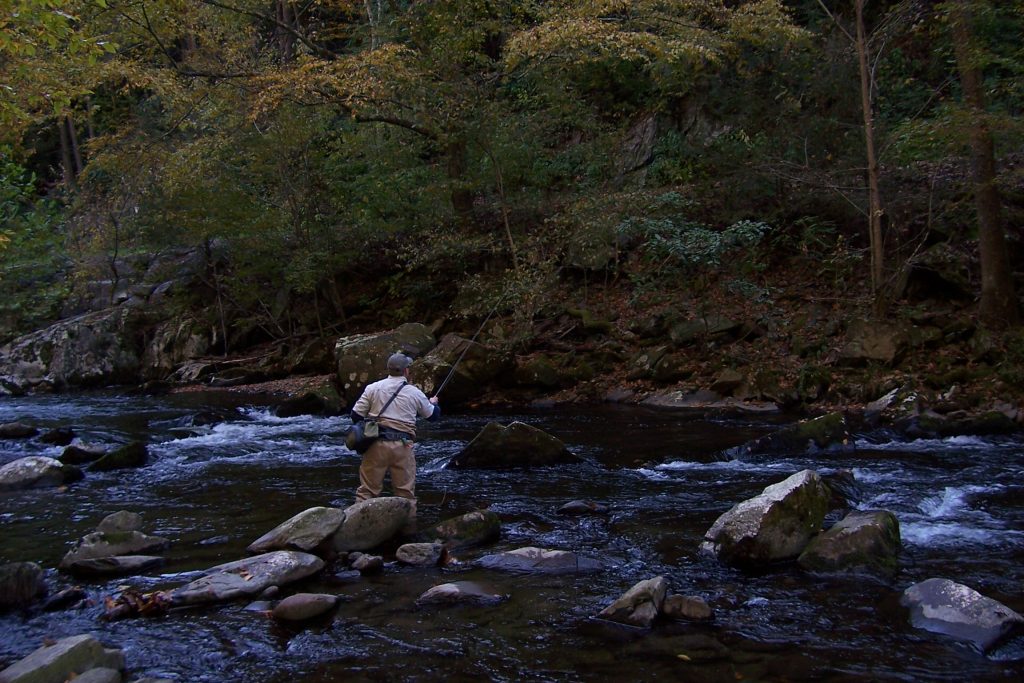
Check out the photo above – a typical stretch of water in the Smokies. You can easily see the numerous changes in current speed and direction in just this small area. Rather than standing at the bottom right of the photo and casting 40-50 feet to the top left of the photo, our angler is intelligently breaking this stretch into defined sections. He has likely already fished the water below, to his left, and right in front of him. Notice he has his rod high, keeping the line off the current directly in front of him, and allowing the fly to drift nicely in the current breaking around the right of the boulder. Next, he will likely step up to the boulder and fish that large pocket above it. Well done! The angler in this photo is also doing a good job with a little more line out. Notice he is concealing himself behind a boulder and his rod is help upward, keeping the current lip in front of him from grabbing the line. The line that is on the water is all in the same current speed. Again, well done!
The angler in this photo is also doing a good job with a little more line out. Notice he is concealing himself behind a boulder and his rod is help upward, keeping the current lip in front of him from grabbing the line. The line that is on the water is all in the same current speed. Again, well done!